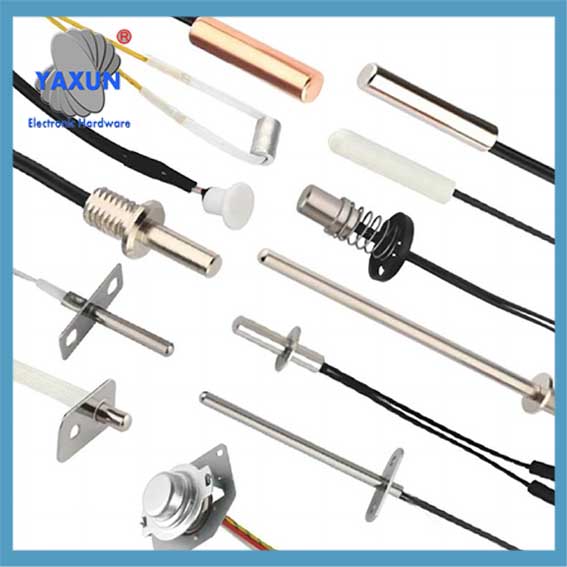
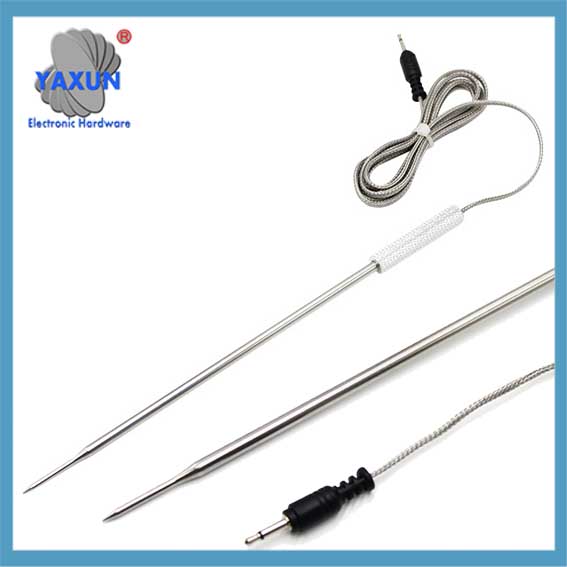
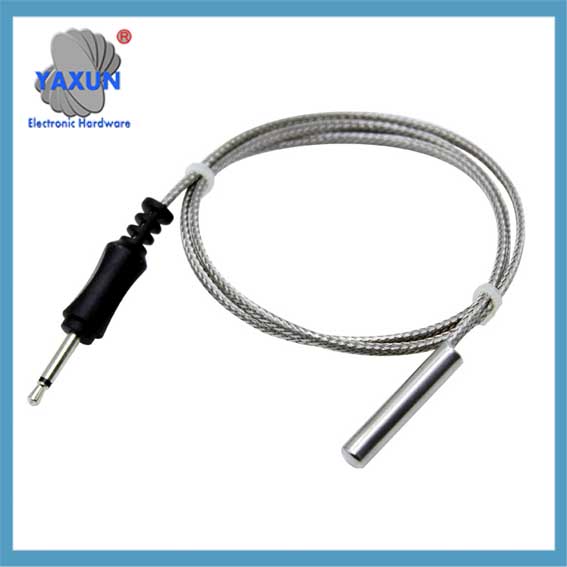
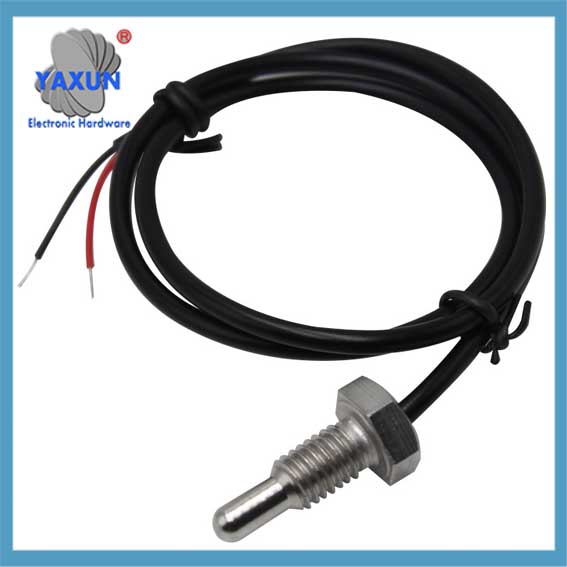
Categorías de Producto
- Disyuntor térmico 20
- Portafusibles 36
- Sensor de temperatura 67
- Interruptor térmico 64
- Fusible del coche 19
- Fusibles atornillados 7
- fusible térmico 32
- fusibles de montaje en superficie 12
- termistor 22
- Portafusibles de montaje en PCB 27
- Arnés de cableado 6
- Portafusibles de cuchilla 17
- termostato 46
- Fusible eléctrico 14
Etiquetas de productos
Mensajes recientes
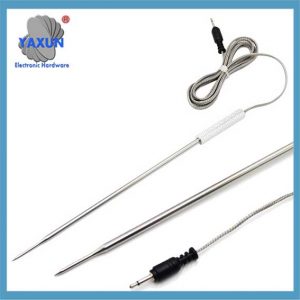
Cable y sonda de sensor NTC personalizados de China
como el sensor, normalmente se divide en: Sonda termistor NTC, sonda PT100, sonda PT1000, sonda ds18b20, sonda de temperatura del agua, sonda de sensor automotriz, Sonda RTD, sonda de control de temperatura, sonda de ajuste de temperatura, sonda del sensor del electrodoméstico, etc..
Sensor probe and cable is the packaging form of the sensor, which is the most basic unit of the sensor. The sensor is packaged through a reasonable electronic circuit and external packaging structure. It has some independent functional components we need. como el sensor, normalmente se divide en: Sonda termistor NTC, sonda PT100, sonda PT1000, sonda ds18b20, sonda de temperatura del agua, sonda de sensor automotriz, Sonda RTD, sonda de control de temperatura, sonda de ajuste de temperatura, sonda del sensor del electrodoméstico, etc..
A NTC probe structure based on temperature prediction and its temperature measurement method, the probe includes: multiple NTC probes; copper shell; metal support structure, wire and heat conductor.
Step 1, among m NTC probes, obtain the temperatures T0, T1, …, Tn measured at equal time intervals through each NTC probe, where n represents the serial number of the collected temperature;
Step 2, calculate the temperature difference vn=TnTn1 collected at adjacent temperature measurement times;
Step 3, calculate the parameter α=vn/vn1;
Step 4, calculate the predicted temperature Tp=Tn1+vn/(1α) of a single probe;
Step 5, calculate the measured temperature Tb. The present invention can further reduce the error and has good general applicability.
Full analysis of thermistors!
🤔 Do you know what a thermistor is? It is a little expert in electronic circuits!
👍 Thermistors, in simple terms, are a type of sensitive element that can adjust its resistance value according to temperature changes.
🔥 Positive temperature coefficient thermistor (PTC), Cuando aumenta la temperatura, its resistance value will increase significantly. This feature makes it shine in automatic control circuits!
❄️ The negative temperature coefficient thermistor (CNT) is the opposite, with the resistance decreasing when the temperature rises. En electrodomésticos, it is often used for soft start, automatic detection and control circuits.
💡 Now you have a deeper understanding of thermistors! In the electronic world, it is an indispensable role!
1. Introduction to NTC
NTC thermistor is a thermistor named after the acronym of Negative Temperature Coefficient. Generalmente, the term “termistor” refers to NTC thermistors. It was discovered by Michael Faraday, who was studying silver sulfide semiconductors at the time, en 1833, and commercialized by Samuel Reuben in the 1930s. NTC thermistor is an oxide semiconductor ceramic composed of manganese (Mn), níquel (En) and cobalt (Co).
It can be seen everywhere in our lives. Due to the characteristic that the resistance decreases with the increase of temperature, it is not only used as a temperature sensing device in thermometers and air conditioners, or a temperature control device in smartphones, kettles and irons, but also used for current control in power supply equipment. Recently, as the degree of vehicle electrification increases, thermistors are increasingly being used in automotive products.
2. Working Principle
Generalmente, the resistance of metals increases as the temperature increases. This is because heat intensifies the lattice vibration, and the average moving speed of free electrons decreases accordingly.
En contraste, the proportion of free electrons and holes in semiconductors increases due to heat conduction, and this part is greater than the proportion of the part where the speed decreases, so the resistance value decreases.
Además, due to the existence of the band gap in semiconductors, when externally heated, electrons in the valence band move to the conduction band and conduct electricity. En otras palabras, the resistance value decreases as the temperature increases.
3. Basic characteristics
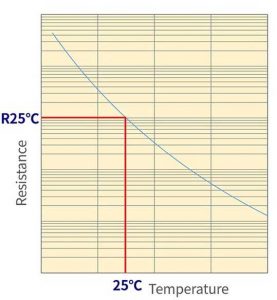
3.1 Resistance-temperature characteristics (R-T characteristics)
The resistance value of an NTC thermistor is measured at a current with sufficiently low self-heating (heat generated due to the applied current). As a standard, it is recommended to use the maximum operating current. And, the resistance value needs to be expressed in pairs with the temperature.
The characteristic curve is described by the following formula:
R0, R1: resistance value at temperature T0, T1
T0, T1: absolute temperature
B: B constante
Cifra 1: R-T characteristic of NTC thermistor
3.2 B constante
The B constant is a single value that characterizes the NTC thermistor. Adjustment of the B constant always requires two points. The B constant describes the slope of the two points.
If the two points are different, the B constant will also be different, so please pay attention when comparing. (See Figure 2)
Cifra 2: Different B constants selected at 2 agujas
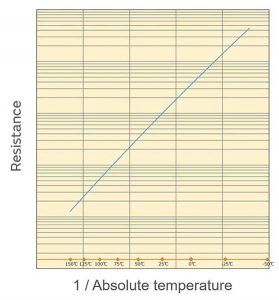
From this, it can be seen that B is the slope of the lnR vs. 1/T curve:
Murata uses 25°C and 50°C to define the B constant, written as B (25/50).
Como se muestra en la figura 3, 1/t (T is absolute temperature) is in logarithmic proportion to the resistance value. It can be seen that the relationship is close to a straight line.
Cifra 3: Temperature characteristics with 1/T as the horizontal axis
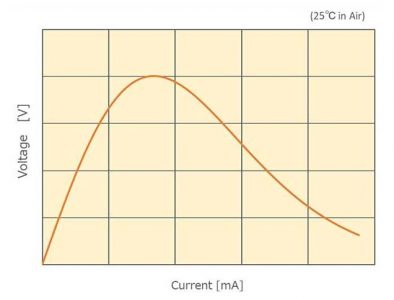
3.3 Volt-ampere characteristics (V-I characteristics)
The V-I characteristics of NTC thermistors are shown in Figure 4.
Cifra 4: V-I characteristics of NTC thermistors
In the area with low current, the voltage of the ohmic contact gradually increases as the current gradually increases. The self-heating caused by the flow of current does not cause the temperature of the resistor to rise by dissipating heat from the surface of the thermistor and other parts.
Sin embargo, when the heat generation is large, the temperature of the thermistor itself rises and the resistance value decreases. In such an area, the proportional relationship between current and voltage no longer holds.
Generalmente, thermistors are used in an area where the self-heating is as low as possible. As a standard, it is recommended that the operating current be kept below the maximum operating current.
If used in an area exceeding the voltage peak, thermal runaway reactions such as repeated heating and reduced resistance may occur, causing the thermistor to turn red or break. Please avoid using it in this range.
3.4 Coeficiente de temperatura de resistencia (α)
The rate of change of the NTC thermistor per unit temperature is the temperature coefficient, which is calculated by the following formula.
Ejemplo: When the temperature is close to 50°C and the B constant is 3380K
α = −3380/(273.15 + 50)² × 100 [%/°C] = −3.2 [%/°C]
Por lo tanto, the temperature coefficient of resistance is as follows.
α = − B/T² × 100 [%/°C]
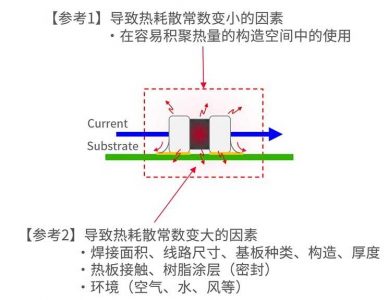
3.5 Thermal dissipation constant (δ)
When the ambient temperature is T1, when the thermistor consumes power P (MW) and its temperature changes to T2, the following formula holds.
P = δ (T2 − T1)
δ is the thermal dissipation constant (mW/°C). The above formula is transformed as follows.
δ = P/ (T2 − T1)
The thermal dissipation constant δ refers to the power required to increase the temperature by 1°C under self-heating conditions.
The thermal dissipation constant δ is determined by the balance between “self-heating due to power consumption” y “heat dissipation”, and therefore varies significantly depending on the thermistor’s operating environment.
Murata defined the concept of “thermal dissipation constant per unit element”.
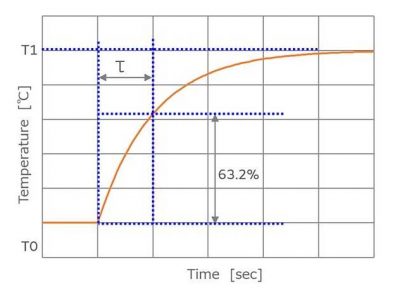
3.6 Constante de tiempo térmico (τ)
When a thermistor maintained at temperature T0 is suddenly changed to ambient temperature T1, the time it takes to change to the target temperature T1 is called the thermal time constant (τ). Generalmente, this value refers to the time required to reach 63.2% of the temperature difference between T0 and T1.
When a thermistor maintained at one temperature (T0) is exposed to another temperature (T1), the temperature changes exponentially, and the temperature (t) after the elapse of time (T) is expressed as follows.
t= (T1 − T0) (1 − exp (−t/τ) ) + T0
Take t = τ,
t= (T1 − T0) (1−1/e) + T0
(T − T0)/(T1 − T0) = 1 − 1/e = 0.632
That is why τ is specified as the time to reach 63.2% of the temperature difference.
Cifra 6: Thermal time constant of NTC thermistor
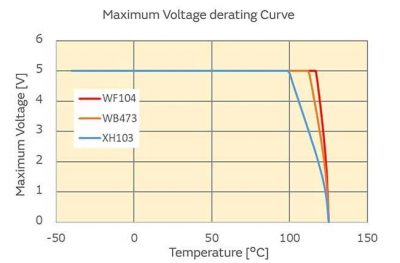
3.7 Maximum voltage (Vmax)
The maximum voltage that can be directly applied to the thermistor. When the applied voltage exceeds the maximum voltage, the product performance will deteriorate or even be destroyed.
Además, the temperature of the component rises due to self-heating. It is necessary to pay attention that the temperature of the component does not exceed the operating temperature range.
Cifra 7: Maximum voltage derating for NCU15 type
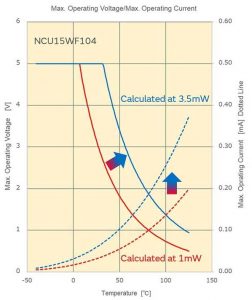
3.8 Maximum operating current (Iop), maximum operating voltage (Vop)
Murata defines the maximum operating current and maximum operating voltage as the current and voltage at which self-heating is 0.1℃ when applied. With reference to this value, thermistors can achieve more accurate temperature measurement.
Por lo tanto, applying current/voltage exceeding the maximum operating current/voltage does not cause thermistor performance degradation. Sin embargo, please note that self-heating of the component will cause detection errors.
How Murata calculates the maximum operating current
When calculating the maximum operating current, the thermal dissipation constant (1mW/°C) defined by the unit component is required. The thermal dissipation constant indicates the degree of heat dissipation, but the heat dissipation state varies greatly depending on the working environment.
The working environment includes the material, espesor, structure, soldering area size, hot plate contact, resin packaging, etc.. of the substrate. The use of the unit component definition eliminates environmental interference factors.
According to experience, the thermal dissipation constant in actual use is about 3 a 4 times that of the unit component. Assuming that the actual thermal dissipation constant is 3.5 veces, the maximum operating current is shown in the blue curve in the figure. Compared with the case of 1mW/°C, it is now 1.9 veces (√3.5 times).
3.9 Zero load resistance value
The resistance value measured at a current (Voltaje) where self-heating is negligible. As a standard, it is recommended to use the maximum operating current.
Cifra 9: Murata’s resistance value measurement method
4. How to use
4.1 Diagrama de circuito
The output voltage may vary depending on the NTC thermistor wiring diagram. You can simulate it at the following URL on the Murata official website.
SimSurfing: NTC Thermistor Simulator (murata.co.jp)
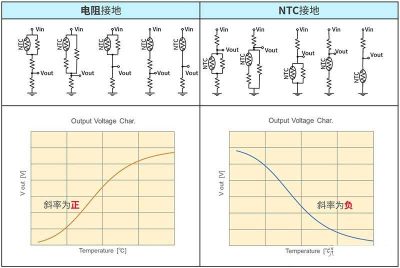
Cifra 10 Output characteristics of resistor grounding and thermistor grounding circuits
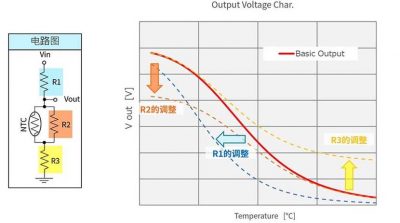
4.2 Adjustment of R1 (voltage divider resistor), R2 (parallel resistor), R3 (series resistor)
The output voltage may vary according to the circuit diagram.
Cifra 11 Adjustment of R value and change of output characteristics
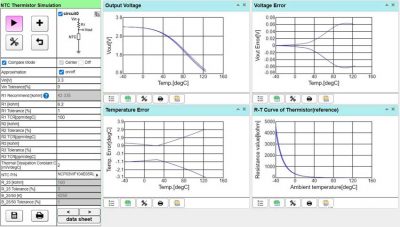
4.3 Calculation of detection error using Murata’s official tool
Select the relevant parameters of the NTC thermistor and the relevant parameters of the voltage divider circuit (reference voltage and voltage divider resistor, resistance accuracy), and then the error curve of temperature detection can be generated normally, Como se muestra en la figura a continuación:
Cifra 12 Generating temperature detection error curve using official tools
Contáctenos
Esperando tu email, le responderemos dentro de 12 horas con la valiosa información que necesitabas.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt