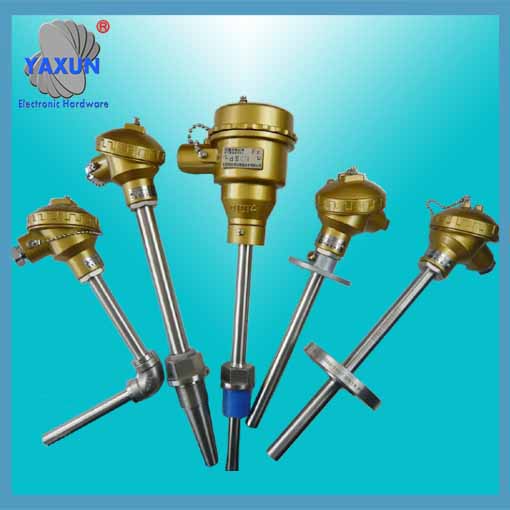
Tuoteryhmät
Tuotetunnisteet
Tarkkuustermoparien toimittaja
Alkuperäinen tehtaalla valmistettu E, J, T-termoelementtianturia käytetään seuraavaan lämpötilan havaitsemiseen: lämpömittari, vedenlämmitin, takka, uuniin, piiri, rtd, kylmä risteys, uuni, yleismittari, digitaalinen, teollinen.
The working principle of E, J, T thermocouple Sensor :
When there are two different conductors or semiconductors A and B forming a loop, the two ends of which are connected to each other, as long as the temperatures at the two junctions are different. The temperature at one end is T, called the working end or hot end, and the temperature at the other end is T0, called the free end (also called the reference end) or cold end. An electromotive force will be generated in the loop. The direction and magnitude of the electromotive force are related to the material of the conductor and the temperature of the two junctions. This phenomenon is called “thermoelectric effect”, and the loop composed of two conductors is called “lämpöpari”. These two conductors are called “thermoelectrodes”, and the electromotive force generated is called “thermoelectromotive force”.
The thermoelectromotive force consists of two parts of electromotive force, one part is the contact electromotive force of two conductors, and the other part is the thermoelectromotive force of a single conductor.
The size of the thermoelectromotive force in the E, J, T thermocouple Sensor loop is only related to the temperature of the conductor material and the two junctions that make up the thermocouple, and has nothing to do with the shape and size of the thermocouple Sensor. When the two electrode materials of the thermocouple Sensor are fixed, the thermoelectromotive force is the difference of the function of the two junction temperature t and t0.
joka on:
This relationship has been widely used in actual temperature measurement. Because the cold junction t0 is constant, the thermoelectromotive force generated by the E, J, T thermocouple only changes with the temperature of the hot junction (measurement end), eli, a certain thermoelectromotive force corresponds to a certain temperature. We can achieve the purpose of temperature measurement as long as we use the method of measuring thermoelectromotive force.
The basic principle of thermocouple temperature measurement is that two conductors of different components form a closed loop. When there is a temperature gradient at both ends, there will be current passing through the loop. Tällä hetkellä, there is an electromotive force-thermoelectromotive force between the two ends, which is the so-called Seebeck effect. Two homogeneous conductors with different components are thermoelectrodes, the end with a higher temperature is the working end, the end with a lower temperature is the free end, and the free end is usually at a certain constant temperature. According to the functional relationship between thermoelectromotive force and temperature, a thermocouple index table is made;
The index table is obtained when the free end temperature is at 0℃, and different thermocouples Sensor have different index tables.
When the third metal material is connected in the thermocouple circuit, as long as the temperature of the two junctions of the material is the same, the thermoelectric potential generated by the thermocouple will remain unchanged. Se on, it is not affected by the access of the third metal in the loop. Siksi, when the thermocouple measures the temperature, the measuring instrument can be connected, and the temperature of the measured medium can be known after the thermoelectromotive force is measured. When the thermocouple measures the temperature, the temperature of its cold junction (the measuring end is the hot end, and the end connected to the measurement circuit through the lead is called the cold junction) is required to maintain the same temperature. Its thermoelectric potential is proportional to the measured temperature. If the (environment) temperature of the cold junction changes during measurement, it will seriously affect the accuracy of the measurement. Take certain measures to compensate at the cold junction, and the influence caused by the temperature change of the cold junction is called the cold junction compensation of the thermocouple is normal. Dedicated compensation wire for connection with measuring instrument.
Calculation method of thermocouple Sensor cold junction compensation:
From millivolt to temperature: Measure the cold junction temperature, convert it to the corresponding millivolt value, add it to the millivolt value of the thermocouple, and calculate the temperature;
From temperature to millivolt: Measure the actual temperature of the cold end temperature, vastaavasti, in terms of millivolts, after subtracting the values derived mV, to obtain the temperature.
Alkuperäinen tehtaalla valmistettu E, J, T-termoelementtianturia käytetään seuraavaan lämpötilan havaitsemiseen: lämpömittari, vedenlämmitin, takka, uuniin, piiri, rtd, kylmä risteys, uuni, yleismittari, digitaalinen, teollinen.
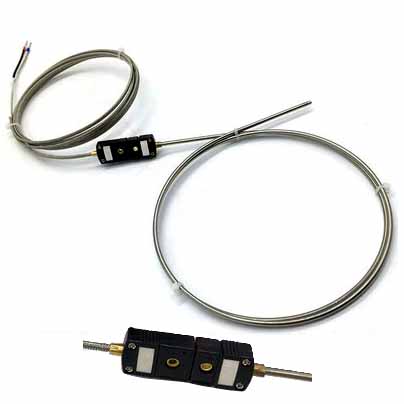

Panssaroidun termoparin halkaisija 3mm + J-tyyppinen pistorasia
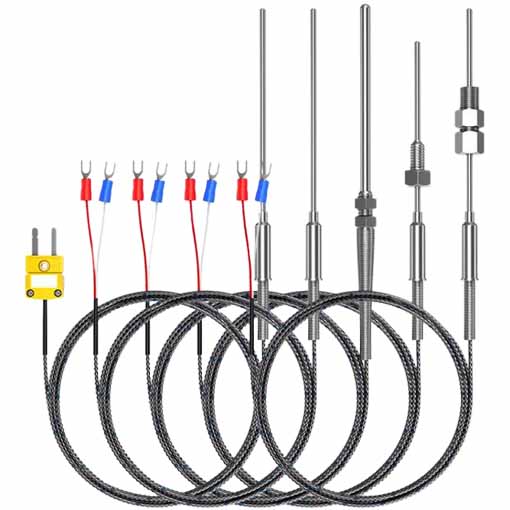
PT100 E, J, T temperature sensor probe
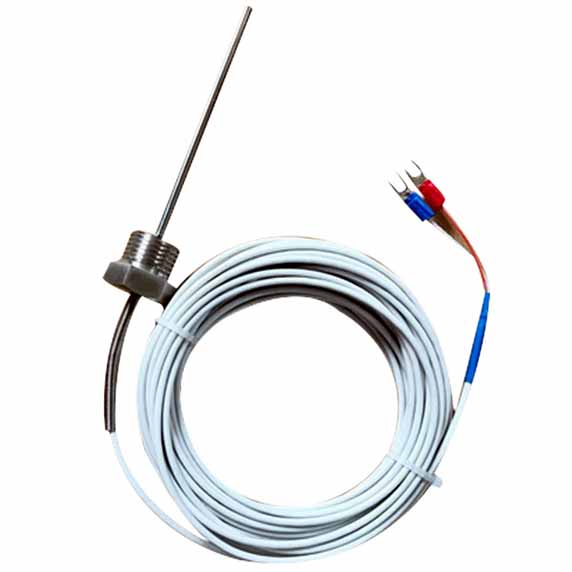

Hot runner thermocouple temperature sensing wire
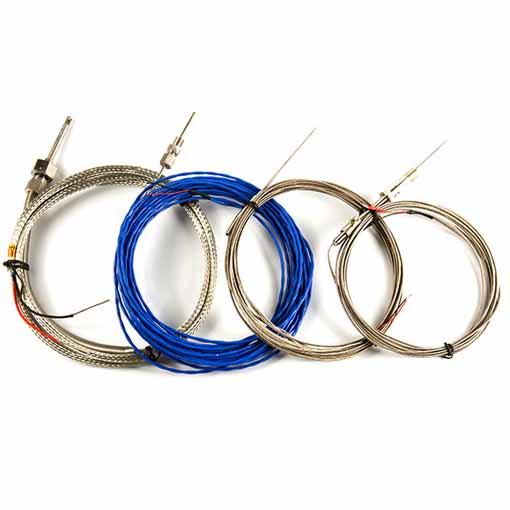

High temperature K-type fast thermocouple
Ota yhteyttä
Sähköpostiasi odotellessa, vastaamme sinulle sisällä 12 tuntia arvokasta tietoa, jota tarvitset.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

