Termékkategóriák
- hőbiztosíték 32
- felületre szerelhető biztosítékok 12
- termisztor 36
- PCB-re szerelhető biztosítéktartó 27
- Kábelköteg 6
- Penge biztosítéktartók 17
- termosztát 50
- Elektromos biztosíték 24
- Autóipari hőmérsékleti érzékelő 7
- Termikus áramkör megszakító 22
- Biztosítékdoboz-tartó 36
- Hőmérséklet érzékelő 75
- Hőkapcsoló 68
- Autó biztosíték 20
- Csavarja le a biztosítékokat 8
Termékcímkék
Egyedi beépített hőbiztosíték csatlakozó és kábel
A hőbiztosíték hővédő. A hőbiztosítékok főként olvadékokból és csövekből állnak, plusz külső töltőanyagok. Használatakor, kösse sorba a hőbiztosítékot a védett áramkörrel. Ha a védett áramkör árama meghaladja a megadott értéket, és egy bizonyos idő elteltével, az olvadék által keltett olvadék maga olvasztja az olvadékot, az áramkör megszakítása, ezáltal védi az áramkört. Azok az elektromos készülékek, amelyek fémvezetőt használnak olvadékként az áramkör megszakításához, sorba vannak kapcsolva az áramkörben.
A beépített hőbiztosíték hővédő. Hőmérséklet A biztosítékok összekötő kábelei főleg olvadékokból és csövekből állnak, plusz külső töltőanyagok. Használatakor, csatlakoztassa sorba a hőbiztosíték összekötő kábelét a védett áramkörrel. Ha a védett áramkör árama meghaladja a megadott értéket, és egy bizonyos idő elteltével, az olvadék által keltett olvadék maga olvasztja az olvadékot, az áramkör megszakítása, ezáltal védi az áramkört. Azok az elektromos készülékek, amelyek fémvezetőt használnak olvadékként az áramkör megszakításához, sorba vannak kapcsolva az áramkörben. Amikor túlterhelés vagy rövidzárlati áram halad át az olvadékon, maga az olvadék felmelegszik és megolvad. Ezért, bizonyos szerepet játszott az energiarendszer védelmében, különféle elektromos berendezések és háztartási gépek. Késleltetés gátló tulajdonsággal, amikor a túlterhelési áram kicsi, a beégetési idő hosszú; Ha nagy a túlterhelési áram, a beégetési idő rövid. Ezért, a túlterhelési áram bizonyos tartományán belül, amíg az áram vissza nem tér a normál értékre, a hőbiztosíték A vezetékköteg nem fog kiégni, és továbbra is használható. A hőmérsékleti biztosíték összeköttetése főként olvadékból áll, egy ház és egy tartó. Köztük, a forró olvadék a kulcsfontosságú elem az olvasztási jellemzők szabályozásában.
Az import- és exportvámokban, kategóriába sorolják őket 8535 vagy 8536.
működési elv
Az áramkörben sorosan olvadékként fémvezetőt használnak. Amikor túlterhelés vagy rövidzárlati áram folyik át az olvadékon, a saját hője miatt összeolvadt, ezáltal megszakad az áramkör. Hőmérséklet biztosíték link egyszerű felépítésű és könnyen használható. Széles körben használják védelmi eszközökként az energiaellátó rendszerekben, különféle elektromos berendezések és háztartási gépek.
Jellemzők
A biztosíték névleges árama nem egyenlő a biztosíték névleges áramával. Az olvadék névleges áramát a védett berendezés terhelési áramának megfelelően választják ki. A biztosíték névleges áramának nagyobbnak kell lennie, mint a biztosíték névleges árama, és a fő elektromos készülékkel együttműködve kell meghatározni.
A beépített hőmérséklet biztosíték összekötő kábele főként olvadékból áll, egy ház és egy tartó. Köztük, az olvadék a kulcsfontosságú komponens az olvadásponti jellemzők szabályozásában. Az anyag, Az olvadék mérete és alakja meghatározza az olvasztási jellemzőket. Az olvadékanyagok két típusra oszthatók, alacsony olvadáspont és magas olvadáspont. Az alacsony olvadáspontú anyagok, például az ólom és az ólomötvözetek alacsony olvadásponttal rendelkeznek, és könnyen megolvaszthatók. Nagy ellenállása miatt, az olvadék keresztmetszeti mérete nagy, és az olvadás során több fémgőz keletkezik. Csak alacsony megszakítóképességű biztosítékokhoz. A magas olvadáspontú anyagok, például a réz és az ezüst magas olvadásponttal rendelkeznek, és nem könnyű megolvasztani. Viszont, alacsony ellenállása miatt, keresztmetszetében kisebbre tehető, mint egy alacsony olvadáspontú olvadék, és az olvasztás során kevesebb fémgőz keletkezik. Alkalmas nagy megszakítóképességű biztosítékokhoz. Az olvadék alakja két típusra oszlik: izzószál és szalag. A változó keresztmetszet alakjának megváltoztatása jelentősen megváltoztathatja a biztosíték jellemzőit.
A hőbiztosítékok késleltetési tulajdonságokkal rendelkeznek, vagyis, amikor a túlterhelési áram kicsi, a biztosíték ideje hosszú; Ha nagy a túlterhelési áram, a beégetési idő rövid. Ezért, egy bizonyos túlterhelési áramtartományon belül, amikor az áram visszatér a normál értékre, a hőbiztosíték összekötő kábele nem fog kiégni, és továbbra is használható. A hőbiztosíték-csatlakozó kábelnek különböző biztosítéki jelleggörbéi vannak, amely a különböző típusú védelmi objektumok igényeihez illeszthető.
hatás
Az áramkörbe beépített elektromos alkatrészek az áramkör biztonságos működésének biztosítása érdekében. Ha az áramkör hibás vagy rendellenes, az áram folyamatosan növekszik, és a megnövekedett áram károsíthatja az áramkör néhány fontos vagy értékes alkatrészét, vagy megégetheti az áramkört, vagy akár tüzet is okozhat. Ha a hőbiztosíték összekötő kábele megfelelően van beszerelve az áramkörbe, a hőbiztosíték összeköttetése magától megolvad, hogy megszakítsa az áramot, ha az áram rendellenesen emelkedik egy bizonyos magasságig és egy bizonyos ideig. Az áramkör biztonságos működésének védelme érdekében. A hőlezárás megszakítja az áramot, ezzel védve az áramkör biztonságos működését.
Szintek közötti együttműködés
A túlzott olvadáspontú olvadás elkerülése és a baleset hatókörének kiterjesztése érdekében, jó koordinációnak kell lennie a felső és az alsó szintek hőbiztosítékai között (azaz, tápvezetékek és mellékvezetékek). Amikor kiválasztja, a felső fokozat biztosíték névleges árama (tápegység fővezeték) hőbiztosíték összekötő kábel kell 1 hogy 2 szakaszai nagyobbak, mint az alsó szakaszé (táp elágazó vezeték). Az általánosan használt hőbiztosítékok az R1 sorozatú cső alakú hőbiztosítékok, Spirális hőbiztosíték RLl sorozat, Tömörített zárt hőbiztosíték RT0 sorozatú és gyors hőbiztosíték RSO, RS3 sorozat, stb.
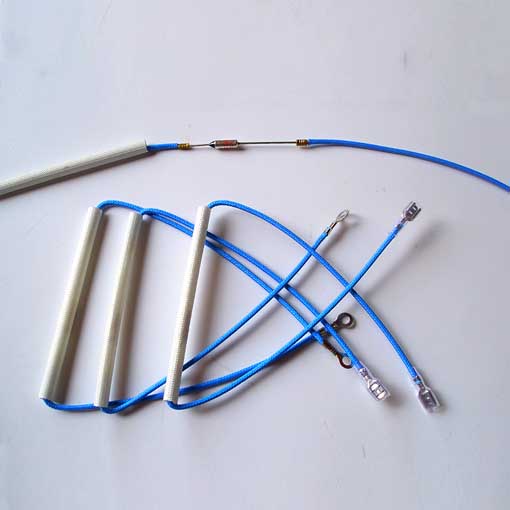

Hőbiztosító vezeték kis háztartási készülékekhez
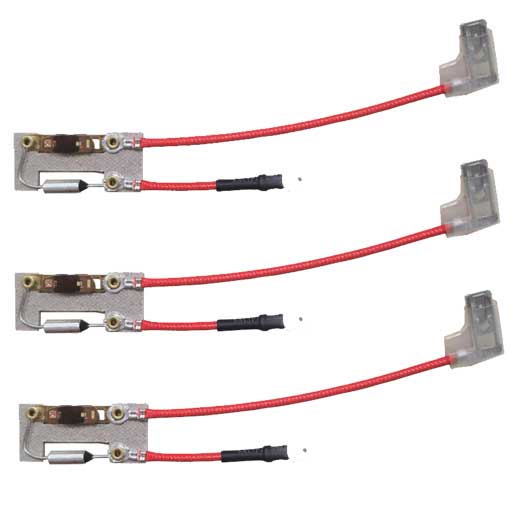

Hőkapcsoló és hőbiztosíték kábelköteg fűtőberendezéshez
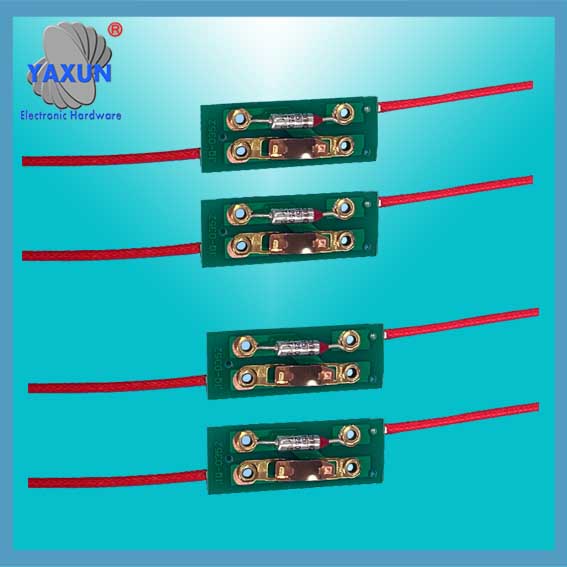
Hőbiztosíték csatlakozó és kábel
Kapcsolódó bemutatkozás
Használat és karbantartás
A kisfeszültségű áramelosztó rendszer hőbiztosítéka olyan elektromos készülék, amely a biztonság védelmében játszik szerepet. A hőbiztosítékkábelt széles körben használják az elektromos hálózat védelmében és az elektromos berendezések védelmében. Ha rövidzárlat vagy túlterhelés lép fel az elektromos hálózatban vagy az elektromos berendezésekben, az áramkör automatikusan lekapcsolható az elektromos berendezések károsodásának elkerülése és a balesetek továbbterjedésének elkerülése érdekében.
A hőbiztosíték szigetelő alapból áll (vagy támogatást), kapcsolatokat, megolvad és így tovább. A biztosíték a biztosíték fő működő része. Az olvadék egyenértékű az áramkörben sorba kapcsolt speciális vezetékkel. Ha az áramkör rövidzárlatos vagy túlterhelt, túl nagy az áramerősség, és az olvadék a túlmelegedés következtében megolvad, ezáltal levágja az áramkört. Az olvadékból gyakran szálakat készítenek, rácsok vagy pelyhek. Az olvadékanyagok alacsony relatív olvadásponttal rendelkeznek, stabil jellemzők és könnyű olvadás. Általában ólom-ón ötvözetet használjon, ezüstözött rézlemez, cink, ezüst és más fémek. Az olvadás és az áramkör levágása folyamatában, ív keletkezik. Az ív biztonságos és hatékony eloltása érdekében, az olvadék általában a biztosítékházba van beépítve, és intézkedéseket tesznek az ív gyors eloltására.
A biztosítékok előnye az egyszerű szerkezet, kényelmes használat, és alacsony ár, és széles körben használják kisfeszültségű rendszerekben.
Hőmérséklet biztosíték Márka: Tamura / Tamura, Albemarle, NEC, Emerson, Panasonic / Matsushita, Xingyu, JingKe, PANASONIC
Első, a hőmérsékletbiztosíték tervezési és működési elve
● A hőmérséklet-biztosíték rendellenes hőmérsékletet észlelt, és lekapcsolta az áramköri funkciót. Érzékeli a háztartási vagy ipari elektromos termékek hőmérsékletét, a rendellenes hőmérséklet-emelkedést, és gyorsan megszakítja az áramkört, el lehet érni, hogy elkerüljük a tűz hatását égetetlen állapotban.
● Hőmérsékleti biztosíték huzal típusa axiális és radiális vezetékkel kettes típussal. Termikus részecskék segítségével (szerves anyag).
● Biztonsági tanúsítvány: UL, CSA, VDE, BABA, PSE, SUGÁRHAJTÁSÚ, CQC ... bizonyítvány, EU ROHS környezetvédelmi irányelvek
● Aktuális termék: 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A
Második, különböző típusú háztartási gépek alkalmazása; mint például a vas, hajszárító (hajszárító), sütő, egyenes haj, porszívók, elektromos melegítők, elektromos ventilátorok Gyümölcscentrifugák, turmixgépek, tápegységek, motorok, nyomtatók, fénymásolók, faxgép, HID ballasztok, fluoreszkáló lámpaelőtétek, transzformátorok, töltő, akkumulátor csomag, fűtőberendezések, elektromos melegítők, rizsfőzők, elektromos termosz, kávéskannák, szellőző ventilátorok, rajongók, varrógépek, vízmelegítők, teljesítmény átalakító , hálózati csatlakozók és aljzatok, hűtőszekrények, klímaberendezések, autóklímák, hangszerek, felszerelés, és a túlmelegedés elleni védelem is.
| modell | Névleges üzemi hőmérséklet (Tf) | Valós üzemi hőmérséklet (Ct) | A hőmérséklet fenntartása (TH) | Hőmérséklet határértéke (TM) | Névleges feszültség (Ur) |
| RF90 | 90℃ | 86±3℃ | 55℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF100 | 100℃ | 96±3℃ | 68℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF110 | 110℃ | 105±3℃ | 75℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF115 | 115℃ | 110±3℃ | 75℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF120 | 120℃ | 116±3℃ | 85℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF125 | 125℃ | 121±3℃ | 90℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF130 | 130℃ | 125±3℃ | 92℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF135 | 135℃ | 131±3℃ | 95℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF140 | 140℃ | 136±3℃ | 100℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF145 | 145℃ | 141±3℃ | 105℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF150 | 150℃ | 146±3℃ | 113℃ | 180℃ | 250V |
| RF155 | 155℃ | 150±3℃ | 113℃ | 200℃ | 250V |
| RF158 | 158℃ | 155±3℃ | 113℃ | 200℃ | 250V |
| RF160 | 160℃ | 157±3℃ | 125℃ | 200℃ | 250V |
| RF165 | 165℃ | 161±3℃ | 125℃ | 200℃ | 250V |
| RF170 | 170℃ | 165±3℃ | 125℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF172 | 172℃ | 167±3℃ | 135℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF175 | 175℃ | 170±3℃ | 135℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF180 | 180℃ | 177±3℃ | 140℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF185 | 185℃ | 181±3℃ | 148℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF188 | 188℃ | 184±3℃ | 148℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF190 | 190℃ | 187±3℃ | 148℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF192 | 192℃ | 189±3℃ | 155℃ | 230℃ | 250V |
| RF195 | 195℃ | 192±3℃ | 155℃ | 250℃ | 250V |
| RF200 | 200℃ | 197±3℃ | 160℃ | 280℃ | 250V |
| RF210 | 210℃ | 205±3℃ | 172℃ | 280℃ | 250V |
| RF216 | 216℃ | 212±3℃ | 175℃ | 280℃ | 250V |
| RF230 | 230℃ | 227±3℃ | 185℃ | 300℃ | 250V |
| RF240 | 240℃ | 235±3℃ | 190℃ | 300℃ | 250V |
| RF250 | 250℃ | 247±3℃ | 208℃ | 320℃ | 250V |
Lépjen kapcsolatba velünk
Várom az e-mailedet, belül válaszolunk 12 óra értékes információkkal, amelyekre szüksége van.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

