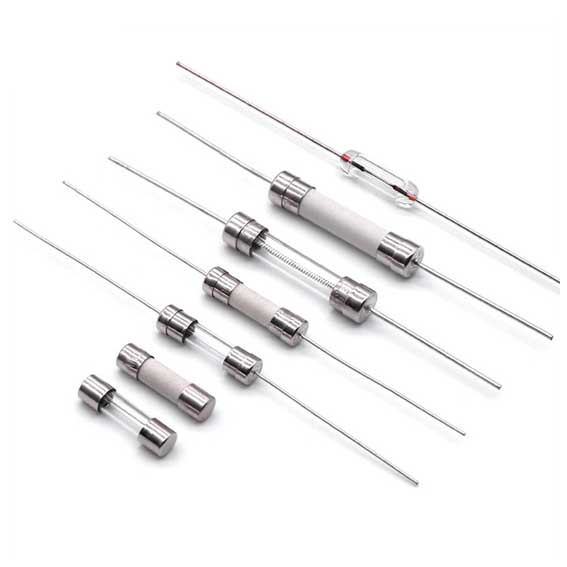
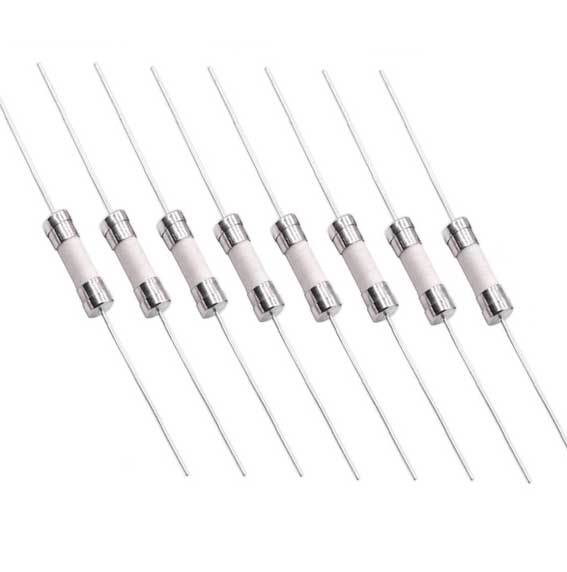
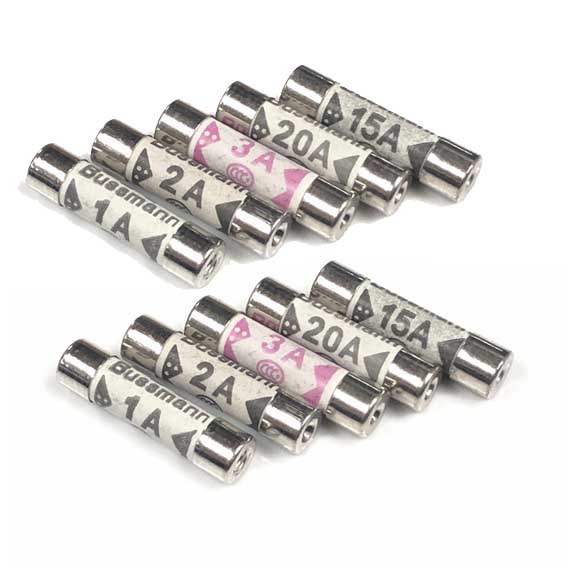
製品カテゴリ
- 温度ヒューズ 32
- 表面実装ヒューズ 12
- サーミスター 36
- PCB マウント ヒューズ ホルダー 27
- ワイヤハーネス 6
- ブレードヒューズホルダー 17
- サーモスタット 50
- 電気ヒューズ 24
- 自動車温度センサー 7
- サーマルサーキットブレーカー 22
- ヒューズボックスホルダー 36
- 温度センサー 75
- サーマルスイッチ 68
- カーヒューズ 20
- ボルトダウンヒューズ 8
製品タグ
カスタムクイック高速/低速セラミック管ヒューズ電流
カスタム 5 * 20mm 6x30mm,6×25mm, 3.6×10mm, 10x38mm セラミックチューブヒューズ ファースト/スローヒューズ リード線とワイヤー付き 250V 0.5A 1A 1.5A 2A 2.5A 3A 4A 5A 6.3A 10A 12A 15A 20A 25A 30A 今日オンライン!
カスタム 5 * 20mm 6x30mm,6×25mm, 3.6×10mm, 10x38mm セラミックチューブヒューズ ファースト/スローヒューズ リード線とワイヤー付き 250V 0.5A 1A 1.5A 2A 2.5A 3A 4A 5A 6.3A 10A 12A 15A 20A 25A 30A 今日オンライン!
Ceramic Tube Fuses define it as a “ヒューズリンク” in international standards. It is an electrical component installed in a circuit to ensure the safe operation of the circuit. Electronic products are all-encompassing, and these products that require electricity must be equipped with the same small components and fuses that are responsible for safety. Not only are there fuses on 3C products, fuses must also be installed on ordinary cars or electric cars.
Now as the products become smaller and smaller, they are more and more integrated, and the shape and size of fuses are also very different from traditional fuses. 例えば, the Ceramic Tube fuse of the mobile phone must conform to the trend of fast charging. To withstand the instantaneous large current, to achieve its protective function, the requirements of fuses are getting higher and higher.
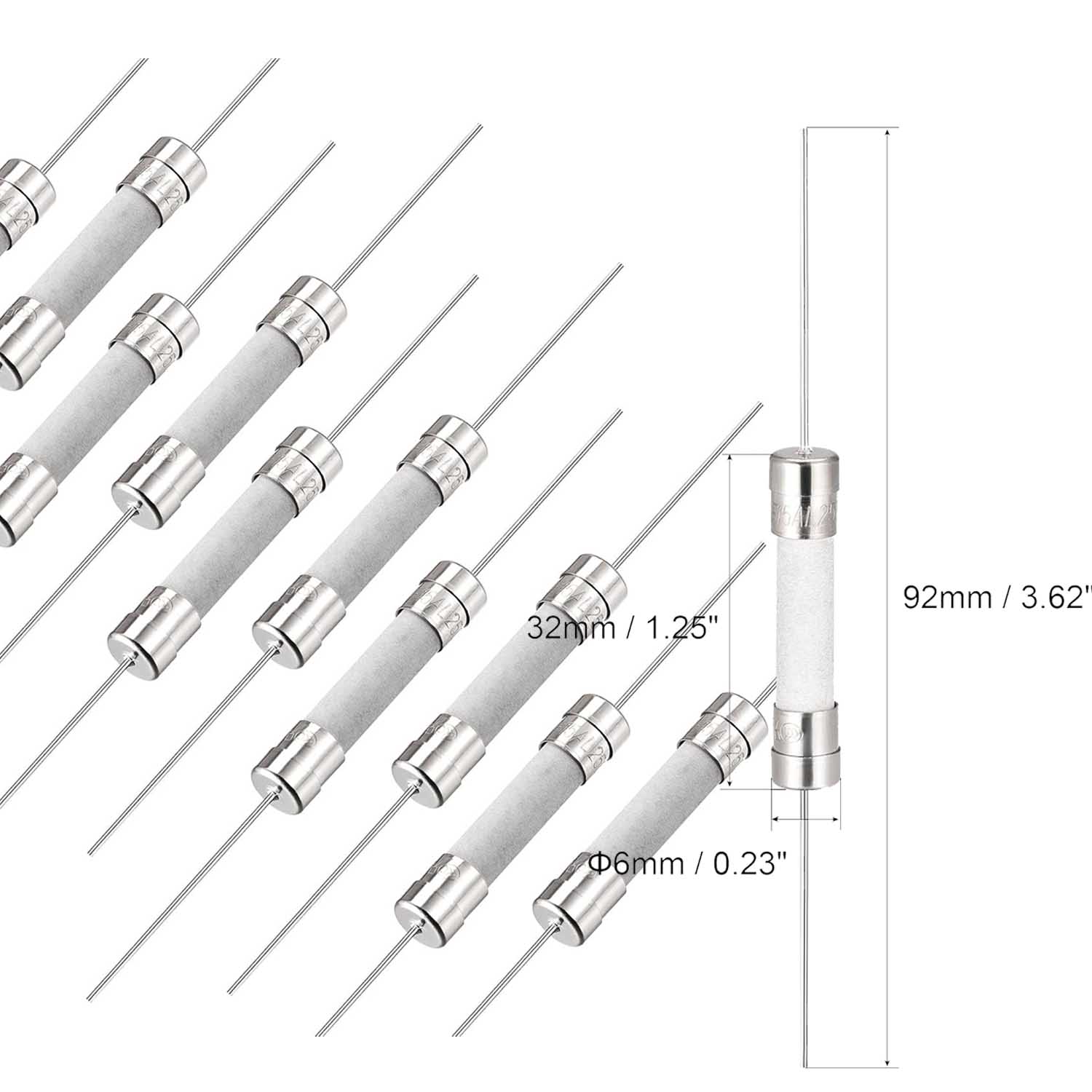
 Time-Lag Slow-Blow 10AMP 250V 5 x 20mm Ceramic Fuses |
 British BS1362 ceramic fuse 6x25MM |
 3.6x10mm Ceramic Tube Fuses With Axial leads |
The glass tube fuses we usually see are not a single material. It is an alloy made of lead, antimony, and tin. This is to achieve the purpose of low melting point and these metals are added, copper caps at both ends, so that the conductivity will be better, the surface of the copper cap is nickel plated.
The shape of the Ceramic Tube fuse has the earliest strip-shaped fuse, which is directly fixed with screws at both ends, and is used on old-style electric brakes.
The chip Ceramic Tube fuse is composed of a plastic sheet and two metal sheets, which are commonly used in automobiles, and glass tubes are often used in electronic products.
Cylindrical fuses will directly solder the pins at both ends to the circuit board. The square fuse has the characteristics of insulation and space saving, and is often used in electronic products such as computers.
The function of the fuse is that when the circuit malfunctions or is abnormal, the current increases continuously, and the increased current may damage the components, burn the circuit or even cause a fire.
If Ceramic Tube fuse is installed in the circuit, when the current abnormally rises to a certain level, the Ceramic Tube fuse is blown to cut off the current and protect the appliance.
Fuses were born in the 1880s. Edison invented Ceramic Tube fuse equivalent to a safety valve in the circuit and applied for a patent. The Ceramic Tube fuse was invented at the time to protect incandescent lamps, because incandescent lamps were very expensive at the time when they were first invented.
With the development of society and the continuous increase of electrical appliances, the Ceramic Tube fuse industry has also developed rapidly. The fuse industry in China started relatively late, and it was not until the 1970s that TV sets were localized that they promoted the development of fuses in China.
The working principle of Ceramic Tube fuse is that when a current passes through a conductor, the conductor will generate heat due to the resistance of the conductor. After the material and shape of the fuse are determined, its resistance is fixed. When current flows through it, it will heat up, and its heat generation will increase with time. The size of the current and resistance determines the rate of heat generation. The structure of the Ceramic Tube fuse and its installation condition determine the rate of heat consumption. If the rate of heat generation is less than the rate of heat dissipation, the fuse will not blow.
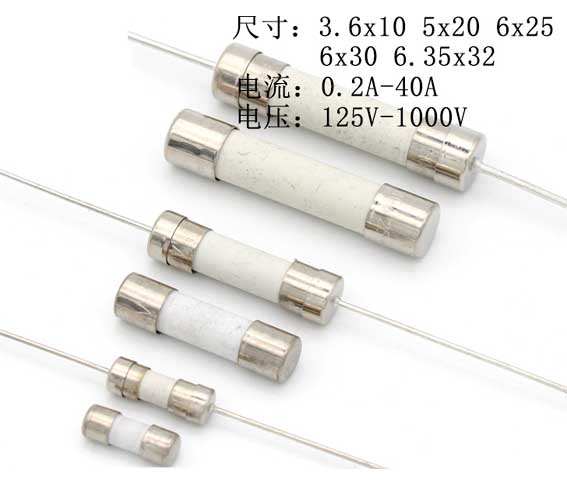

セラミックチューブヒューズは高速です – 遅いヒューズ
If the rate of heat generation is equal to the rate of heat dissipation, it will not melt for a long time. If the rate of heat generation is greater than the rate at which heat disappears, the amount of heat generated will increase and the increase in heat will cause the temperature to rise. When the temperature rises above the fuse’s melting point, the fuse will blow.
Manufacture of common glass tube fuses. The silicon dioxide material is first drawn into a transparent glass tube with a diameter of 5 mm through high temperature, and then cut into a length of 20 んん. The two ends of the glass tube must be rounded with high temperature to avoid the sharp edges of the glass tube from scratching the fuse when passing through the fuse.
An alloy fuse is placed in the glass tube, and the printed top and bottom covers are welded together with the Ceramic Tube fuse by high frequency.
ついに, the machine automatically detects the Ceramic Tube fuse, pops out the unqualified fuse, and packs the qualified fuse.
Some people may wonder why the common Ceramic Tube fuse is installed in a glass tube. 初め, the glass tube is insulated and difficult to ignite, ensuring that the fuse is the only conductive connection intermediary at both ends. The cheap price of glass tube is also the reason to use it. 加えて, the glass tube can see whether the internal fuse is blown, it is relatively easy to judge the quality of the fuse, and the glass tube is not vacuum.
テクノロジーの発展に伴い, more types of fuses have appeared. Such as the resettable fuse, this type of fuse is automatically deformed when the temperature exceeds a certain safe temperature, leading to power failure. After the temperature is restored, it can be automatically powered on to work normally without manual intervention.
Product Details
Intentions to develop, テクノロジーを社会に役立てるために
| 遮断容量 | 材料 | 動作温度 | はんだ付け条件 |
| 1500A at 250V AC(1A-10A) | Fuse body –ceramic tube エンドキャップ–ニッケルメッキ真鍮 ピグテール–ニッケルメッキ真鍮キャップに錫メッキ銅 |
-40℃~+125℃ | ウェーブはんだ:260℃,≤5S 手はんだ: 360℃,≤1S |
機能特性
| 試験電流 | ブロータイム | |
| 分 | マックス | |
| 150% | 1 時間 | – |
| 210% | 1 S | 30分 |
| 275% | 750MS | 80s |
| 400% | 95MS(1A-3.15A) 150MS(4A-16A) |
5S(1A-10A) 8S(12.5A-16A) |
| 1000% | 10 MS | 150MS |
承認(○保留中の●承認)
| 電流定格 | 定格電圧 | 通常の融解 I2T(A2秒) | 承認 | |||||
| VDE | CCC | CQC | UL | PSE | KC | |||
| 1あ | 250V | 1.4 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| 1.25あ | 250V | 2.0 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 1.6あ | 250V | 3.3 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 2あ | 250V | 5.2 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 2.5あ | 250V | 8.3 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 3.15あ | 250V | 13 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 4あ | 250V | 22 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 5あ | 250V | 36 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 6.3あ | 250V | 54 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 8あ | 250V | 90 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 10あ | 250V | 130 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| 12あ | 250V | 112 | ○ | ● | ||||
| 12.5あ | 250V | 216 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ● | ○ | |
| 15あ | 250V | 252 | ○ | ● | ||||
| 16あ | 250V | 332 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||
お問い合わせ
メールを待っています, 以内に返信させていただきます 12 必要な貴重な情報を何時間も入手できる.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt