제품 카테고리
- 온도 퓨즈 32
- 표면 마운트 퓨즈 12
- 서미스터 36
- PCB 마운트 퓨즈 홀더 27
- 배선 하니스 6
- 블레이드 퓨즈 홀더 17
- 온도 조절기 50
- 전기 퓨즈 24
- 자동차 온도 센서 7
- 열 회로 차단기 22
- 퓨즈 박스 홀더 36
- 온도 센서 75
- 열 스위치 68
- 자동차 퓨즈 20
- 퓨즈를 볼트로 낮추십시오 8
제품 태그
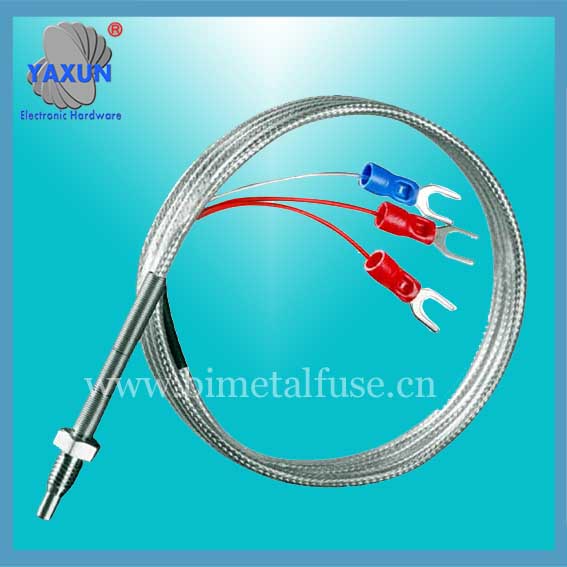
RTD PT100 온도 센서 프로브(케이블 포함)
백금 열저항 센서란??
RTD (저항온도검출기) 온도 변화에 따라 저항이 변하는 백금 열 저항입니다.. 센서 온도가 증가하면 저항이 증가합니다.. 저항과 온도 사이의 관계는 잘 알려져 있으며 시간이 지남에 따라 반복 가능합니다.. RTD는 수동 장치입니다.. 자체적으로 출력을 생성하지 않습니다.. 외부 전자 장치를 사용하면 센서에 작은 전류를 통과시켜 전압을 생성함으로써 센서 저항을 측정할 수 있습니다.. 일반적으로 1 mA 이하의 측정 전류, 최고 5 엄마, 자체 발열 위험 없이.
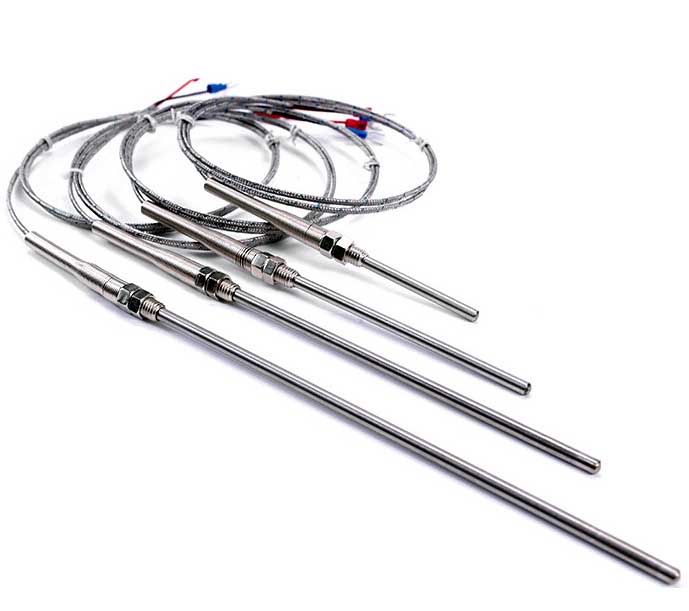
백금 내열성 온도 감지기 (PT100 RTD) 온도에 비례하여 저항을 변화시켜 온도를 측정하는 센서입니다.. RTD PT100은 기본 온도 요소와 완전한 프로브 및 배선 하니스 어셈블리로 설계되었습니다.. 이러한 소위 RTD 프로브는 백금 열 저항 요소로 구성됩니다., 덮개 또는 하우징, 에폭시 또는 충전재, 연장 리드, 때로는 커넥터 또는 종단. 재료 호환성에 대한 고객 요구 사항에 따라 다양한 센서 재료를 사용할 수 있습니다., 정확도 및 측정 범위. 표준 키트 및 맞춤형 설계는 다양한 응용 분야에 가장 적합한 RTD 온도 센서를 설계할 수 있는 유연성을 제공합니다..
RTD PT100 온도 센서 및 프로브는 다양한 산업 분야의 다양한 응용 분야에 통합될 수 있습니다.. 이 온도 센서는 보드 장착 압력 부품에서 작동하도록 여러 기관의 인증을 받았습니다.; 가혹하고 위험한 환경에서도 작동 가능. 당사의 광범위한 온도 센서 제품 옵션은 의료를 포함한 까다로운 OEM 응용 분야의 특정 감지 요구 사항을 해결합니다., 항공우주, 자동차, 수단, 가전제품, 모터 제어, HVAC 및 냉동 시스템.
RTD PT100 표준 공차
RTD는 여러 표준화된 곡선 및 허용 오차에 맞춰 제작되었습니다.. 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 정규화 곡선은 “에서” 곡선. 이 곡선은 백금의 저항 대 온도 특성을 설명합니다. 100 옴 센서, 표준화된 공차, 측정 가능한 온도 범위.
DIN 표준은 다음과 같은 기본 저항을 지정합니다. 100 0°C에서 옴, 온도 계수는 다음과 같습니다. 0.00385 옴/옴/°C. DIN RTD 센서의 공칭 출력은 다음과 같습니다.:
DIN RTD에는 세 가지 표준 공차 등급이 있습니다.. 이러한 공차는 다음과 같이 정의됩니다.:
DIN 클래스 A: ±(0.15 + 0.002 |티|℃)
DIN 클래스 B: ±(0.3 + 0.005 |티|℃)
DIN 클래스 C: ±(1.2 + 0.005 |티|℃)
0°C/옴
0: 100.00
10: 103.90
20: 107.79
30: 111.67
40: 115.54
50: 119.40
60: 123.24
70: 127.07
80: 130.89
90: 134.70
100: 138.50
RTD 구성 요소 유형
RTD 요소의 유형을 결정할 때, 먼저 센서를 읽는 데 사용되는 장비를 고려하십시오.. 기기의 센서 입력과 호환되는 구성 요소 유형을 선택하세요.. 지금까지 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 RTD는 다음과 같습니다. 100 온도 계수를 갖는 옴 백금 0.00385.
구성 요소 유형 기본 저항기 (옴) TCR (옴/옴/°C)
백금 100 0°C에서 옴 .00385
백금 100 0°C에서 옴 .00392
백금 100 0°C에서 옴 .00375
니켈 120 0°C에서 옴 .00672
구리 10 25°C에서 옴 .00427
RTD 정확도
두번째, 필요한 측정 정확도 결정. 정확도는 기본 저항 허용 오차의 조합입니다. (교정 온도에서의 저항 허용오차) 저항기 공차 온도 계수 (특성 경사 공차). 이보다 높거나 낮은 온도는 허용 범위가 더 넓거나 정확도가 떨어집니다. (아래 그림 참조). 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 교정 온도는 0°C입니다..
RTD PT100 센서는 여러 가지 리드 구성으로 제공됩니다.. 가장 일반적인 구성은 단일 요소 3리드 구성입니다.. 사용 가능한 리드 구성의 개략도는 다음과 같습니다.:
PT100/PT1000 2선 센서는 일반적으로 정확도가 중요하지 않은 응용 분야에 사용됩니다.. 2선 구성으로 가장 간단한 측정 기술이 가능합니다., 그러나 센서 리드의 저항으로 인해 본질적인 부정확성이 있습니다.. 2선 구성, 저항 측정에서 오프셋 증가를 유발하는 리드 저항을 직접적으로 보상하는 것은 불가능합니다..
PT100/PT1000 3선 센서에는 측정 중 리드 저항을 제거할 수 있는 보상 루프가 있습니다.. 이 구성으로, 컨트롤러/측정 장치는 두 가지 측정을 수행할 수 있습니다.. 첫 번째 측정의 경우, 센서와 연결 리드의 총 저항을 측정합니다.. 두 번째 측정 중, 보상 루프 저항기의 저항을 측정합니다.. 실제 순 저항은 총 저항에서 보상 루프 저항을 빼서 결정됩니다.. 3선 센서는 가장 일반적인 구성이며 정확성과 편의성이 적절히 조합되어 있습니다..

PT100 온도 센서

PT100 센서 프로브
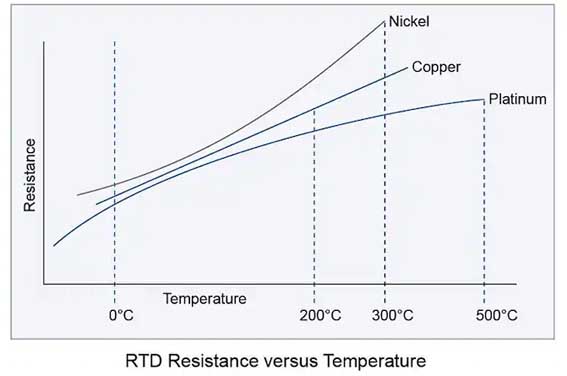
RTD 저항 대 온도
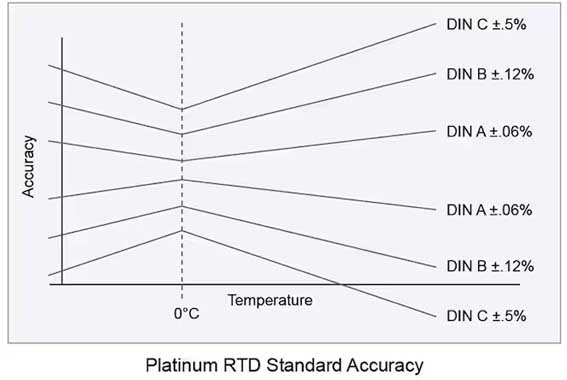
플래티넘 RTD 표준 정확도
PT100/PT1000 4선식 센서 구성 및 측정 기술은 리드의 영향을 받지 않고 센서 저항을 측정합니다.. 이 기술이 더 정확하지만, 많은 산업용 컨트롤러/측정 장치는 진정한 4와이어 측정을 달성할 수 없습니다..
센서 리드에서 현장 배선으로의 전환은 일반적으로 센서에 연결되는 커넥터에서 수행됩니다.. 쉬운 연결을 위해 터미널 블록이 제공됩니다..
저항온도검출기로 온도를 측정하는 것은 실제로 저항을 측정하는 것입니다.. 불균형 휘트스톤 브리지는 종종 저항을 측정하는 데 사용됩니다.. 감지 요소의 저항을 측정하는 경우, 정확한 판독값을 얻으려면 모든 외부 요인을 최소화하거나 보상해야 합니다..
오류의 주요 원인 중 하나는 리드의 저항일 수 있습니다., 특히 2리드 구성에서.
저항기는 감지 요소와 직렬로 연결됩니다., 따라서 판독값은 감지 요소와 리드 저항의 합입니다.. 2리드 RTD는 감지 요소의 저항이 높고 리드의 저항이 낮을 때 사용할 수 있습니다..
하지만, 리드의 저항이 상대적으로 높을 때, 그것은 보상받아야 한다. 보상은 3리드 구성으로 제공됩니다.. 3리드 다이어그램에 표시된 대로, 전원 공급 장치의 한쪽은 L3을 통해 RTD의 한쪽에 연결됩니다.. 이렇게 하면 L1과 L2가 브리지의 반대편에 놓이게 됩니다., 그래서 그들은 서로 상쇄되고 브리지 출력 전압에 영향을 미치지 않습니다..
RTD에는 3리드 연결을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다., 특히 감지 요소 저항이 낮은 경우, 작은 리드 저항이 판독 정확도에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있는 경우.
문의하기
이메일을 기다리는 중, 이내에 답변해 드리겠습니다. 12 필요한 귀중한 정보를 몇 시간 동안.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

