The principle of NTC thermistor is that when the power switch is turned on, the NTC thermistor is in a cold state and has a large resistance value, which can effectively suppress the surge pulse current flowing through the resistor. Under the dual effects of surge pulse current and working current, the temperature of the NTC thermistor will rise. Because it has a negative temperature coefficient characteristic, the temperature rises and the resistance value drops sharply.
NTC thermistors can be used in AC lines or in the DC output of bridge rectifiers to suppress the startup surge current.
Its working principle is: when the power switch is turned on, the NTC thermistor is in a cold state and has a large resistance value, which can effectively suppress the surge pulse current flowing through the resistor. Under the dual effects of surge pulse current and working current, the temperature of the NTC thermistor will rise. Because it has a negative temperature coefficient characteristic, the temperature rises and the resistance value drops sharply. Under steady-state load current, its resistance value will be very small, only about 1/20~1/50 of that in cold state, and the limiting effect on current will be small, the power consumption is very small, and it will not affect the efficiency of the entire power supply. Daarom, when used in the same circuit of the power supply, the power-type NTC thermistor of Heng Electronics is the simplest and most effective measure to suppress the startup surge current and protect electronic equipment from damage. The MF72, MF73, and MF74 series NTC thermistors are used in surge suppression.
NTC thermistor temperature measurement range
In werkelijke toepassingen, what is the operating temperature range of NTC thermistors? In what range is it safe? Hier, YAXUN Electronics NTC thermistors are used as an example to analyze the operating temperature range of NTC thermistors.
In werkelijke toepassingen, the power-type NTC thermistor should be operated within the rated operating temperature range as much as possible. If the upper and lower temperature limits are exceeded, the power-type NTC product may fail or be damaged.
• Be careful not to operate it in a humid environment, because an overly humid environment will accelerate the aging of the power-type NTC thermistor.
• Since power NTC thermistors are greatly affected by ambient temperature, the maximum steady-state current at room temperature (0-25°C) is generally given in the product specification.
• Some foreign brands of power NTC thermistor products give the maximum steady-state current at 0-65°C, which is more in line with the actual state of the product.
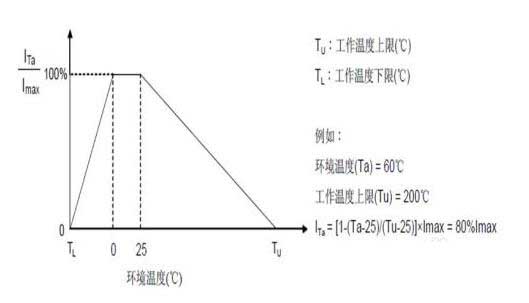
• The maximum current derating curve of power NTC thermistors is shown in the figure below. Under the highest or lowest operating temperature conditions, the rated current will be linearly reduced to zero.
• The application conditions of power NTC thermistor products are not at room temperature (0-25°C), or due to the design or structure of the product itself, such as there are some devices with high heat generation in the power supply. When the ambient temperature is too high or too low, it must be used at a derating rate according to the current reduction curve.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt