Product Categories
Product Tags
Thermal Cut-Off (TCO) is an overheat protection component. When the temperature inside the device or system exceeds the preset safety value, the TCO disconnects the circuit to prevent damage to the device or fire. This type of fuse is often used in electronic equipment, automobiles, and industrial equipment to provide additional safety. This article summarizes the working principle, structural characteristics, process flow, selection parameters, and design considerations of the thermal fuse.
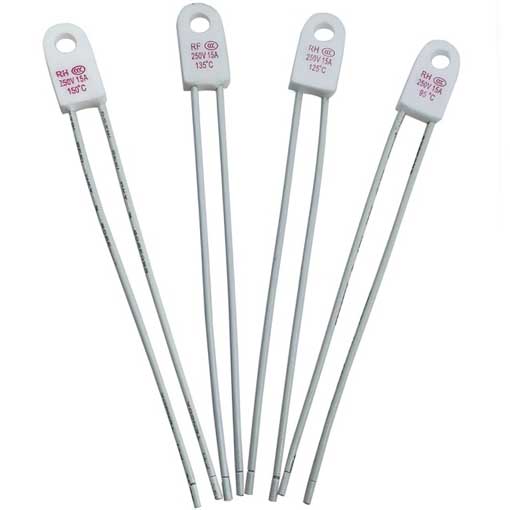

TAMURA / SET Thermal Fuse Pin Up Type
Notes on the installation of thermal fuse:
1. When using lead bending, it should be bent from a part more than 6 mm from the root; When bending, do not damage the roots and leads, and do not pull, press, or twist the leads forcibly.
2. When the thermal fuse is fixed by screws, riveting or binding posts, it should be able to prevent mechanical creep and poor contact.
3. The connecting parts should be able to work reliably within the working range of the electrical product without displacement due to vibration and shock.
4. When welding the lead wire, the heating humidity should be limited to a minimum, and no high temperature should be applied to the thermal fuse; Do not forcibly pull, press, or twist thermal fuses and leads; After welding, it should be cooled for more than 30 seconds immediately.
5. The thermal fuse can only be used under the conditions of the specified rated voltage, current and specified temperature. Pay particular attention to the maximum continuous temperature that the thermal link can withstand.
Note: Nominal current, lead length and temperature can be Designed according to customer requirements.
N-F Series
Thermal Fuse Features
Fusing temperature thermal fuse accurate, high withstand voltage, small size, and temperature resistance.
Belonging unrecoverable type thermal fuses. Temperature fuse melting off, even if the surrounding temperature falls, it will not be turned on.
Use insulating housing.
No lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd), and comply with RoHS.
REACH does not contain the specified 46 categories SVHC (SVHC).
Thermal Fuse Size
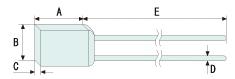
TAMURA Thermal Fuse
| Cable length | Dimensions (mm) | ||||
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| Standard N-F | 4.1±0.1 | 5.2±0.1 | 2.0±0.1 | 0.53±0.05 | 36±3.0 |
| Long N-F(L) | 4.1±0.1 | 5.2±0.1 | 2.0±0.1 | 0.53±0.05 | 68±3.0 |
| Model | Rated temperature Tf(℃) |
Operating temperature (℃) |
Rated current (A) |
Rated voltage (V) |
maintaining the temperature Th(℃) |
Maximum temperature limit Tm(℃) |
| N06F | 65 | 61±3 | 1.0 | AC250 | 50 | 200 |
| N0F | 76 | 72±3 | 1.0 | AC250 | 50 | 200 |
| N1F | 86 | 81±2 | 1.0 | AC250 | 60 | 200 |
| N2F | 102 | 98±3 | 1.0 | AC250 | 75 | 200 |
| N3F | 115 | 111±2 | 1.0 | AC250 | 95 | 200 |
| N4F | 127 | 123±2 | 1.0 | AC250 | 105 | 200 |
| N13F | 133 | 129±3 | 1.0 | AC250 | 105 | 200 |
| N5F | 136 | 131±2 | 1.0 | AC250 | 100 | 200 |
| N6F | 139 | 134±2 | 1.0 | AC250 | 110 | 200 |
| N7F |
Contact Us
Waiting for your email, we will reply you within 12 hours with valuable information you needed.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt


