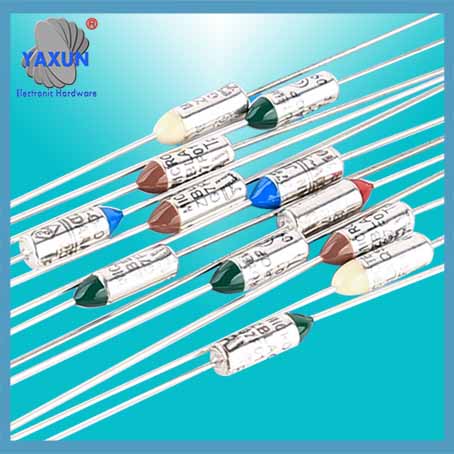
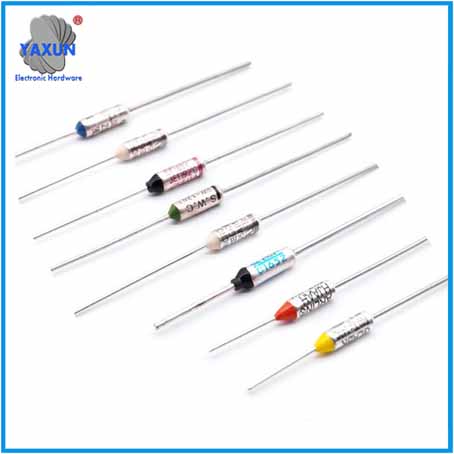
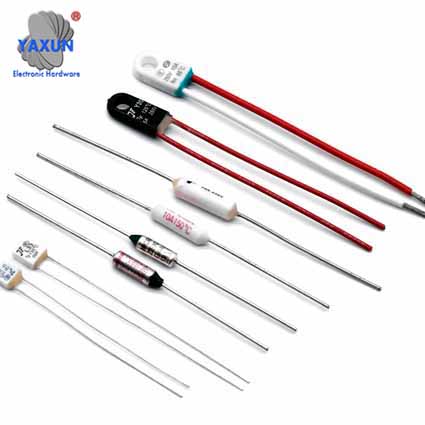
Product Categories
Product Tags
Thermal Fuse Function and Application
The Thermal Fuse (Thermal Cutoff, Temperature Fuse) is Axial / Radial / Organic Thermal-Link(OTCO) safety parts that stops the flow of electricity to the motor circuit when a overheats. If the fuse is missing or broken, your motor will not start. The thermal fuse is sensitive to external temperature, and the operating temperature is accurate and stable. Small size, sealed structure. Reliable performance. Low resistance value. One-time action cuts off the current, and the current interruption capacity reaches 250VAC/25A.
The thermal fuse has safety certifications UL(C-UL), VDE,CCC, KTL, PSE and complies with RoHS standards. The Thermal Fuse (Thermal Cutoff, Temperature Fuse) is Axial / Radial / Organic Thermal-Link(OTCO) safety parts that stops the flow of electricity to the motor circuit when a overheats. If the fuse is missing or broken, your motor will not start.
The thermal fuse is sensitive to external temperature, and the operating temperature is accurate and stable. Small size, sealed structure. Reliable performance. Low resistance value. One-time action cuts off the current, and the current interruption capacity reaches 250VAC/25A.
A thermal fuse fails when the exhaust temperature exceeds the Thermal fuse rating, that is when the temperature rises above the Set temperature that the fuse is designed to handle.
This can Circuit break occur when a heating element is shorted, a regulating thermostat or thermister fails, or with a partially restricted exhaust vent.
The Thermal Fuse attaches to the blower wheel housing. It must be replaced when there is no longer continuity between the terminals. This is a one-time Thermal Fuse, meaning it cannot be re-set. The replacement part features Same current and temperature characteristics.
Uses of thermal fuses:
Coil products: transformers, motors, chargers Network communication equipment: routers, switches Home appliances: TVs, air conditioners, washing machines Audio-visual equipment: cameras, monitors, DVDs Office equipment: computers, printers, copiers Information electronic products: mobile phones, PDAs.
Current characteristics
SD&TD series: 10A/15A
PD&QD series: 20A/25A
TS series: 100A
PD&QD Thermal Fuse series
 10A/15A thermal fuse | 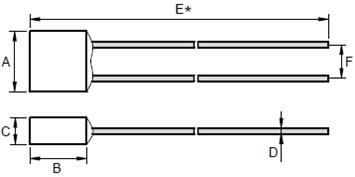 Thermal fuse for rice cooker and dryer | Dimensions(mm)
|
| Model NO. | Tf (℃) | Fuse-Temp(℃) | TH(℃) | TM (℃) | Ir (A) | Ur (V) | RoHS |
| PD102 | 102 | 98±2 | 66 | 160 | 20 | 125DC | ▲ |
| PD115 | 115 | 111±2 | 82 | ▲ | |||
| PD125 | 125 | 121±2 | 90 | ▲ | |||
| PD130 | 130 | 125±2 | 97 | ▲ | |||
| PD136 | 136 | 131±2 | 102 | ▲ | |||
| PD150 | 150 | 145±2 | 117 | ▲ | |||
| QD102 | 102 | 98±2 | 66 | 160 | 25 | 125DC | ▲ |
| QD115 | 115 | 111±2 | 82 | ▲ | |||
| QD125 | 125 | 121±2 | 90 | ▲ | |||
| QD130 | 130 | 125±2 | 97 | ▲ | |||
| QD136 | 136 | 131±2 | 102 | ▲ | |||
| QD150 | 150 | 145±2 | 117 | ▲ | |||
PD&QD Thermal Fuse series
 High current thermal fuse | 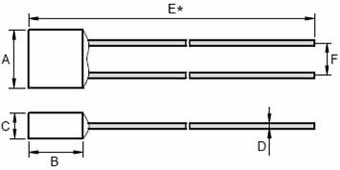 Thermal cut-off of high current | Dimensions(mm)
|
| Model NO. | Tf (℃) | Fuse-Temp(℃) | TH(℃) | TM (℃) | Ir (A) | Ur (V) | RoHS |
| PD102 | 102 | 98±2 | 66 | 160 | 20 | 125DC | ▲ |
| PD115 | 115 | 111±2 | 82 | ▲ | |||
| PD125 | 125 | 121±2 | 90 | ▲ | |||
| PD130 | 130 | 125±2 | 97 | ▲ | |||
| PD136 | 136 | 131±2 | 102 | ▲ | |||
| PD150 | 150 | 145±2 | 117 | ▲ | |||
| QD102 | 102 | 98±2 | 66 | 160 | 25 | 125DC | ▲ |
| QD115 | 115 | 111±2 | 82 | ▲ | |||
| QD125 | 125 | 121±2 | 90 | ▲ | |||
| QD130 | 130 | 125±2 | 97 | ▲ | |||
| QD136 | 136 | 131±2 | 102 | ▲ | |||
| QD150 | 150 | 145±2 | 117 | ▲ | |||
TS series Thermal Fuse
 Customized thermal fuse | Dimensions(mm) 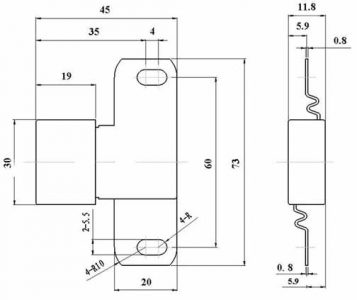 Thermal Fuse Size |
| Model | Tf (℃) | Fuse-Temp (℃) | TH (℃) | TM (℃) | *Imax 8/20us (1 time) | Ir (A) | Ur (V) | RoHS |
| TS102 | 102 | 99±2 | 61 | 180 | 100KA | 80 | 250(AC) | ▲ |
| 100 | 125(AC) | ▲ | ||||||
| 100 | 100(DC) | ▲ | ||||||
| TS115 | 115 | 112±2 | 74 | 180 | 100KA | 80 | 250(AC) | ▲ |
| 100 | 125(AC) | ▲ | ||||||
| 100 | 100(DC) | ▲ | ||||||
| TS123 | 123 | 118±2 | 82 | 180 | 100KA | 80 | 250(AC) | ▲ |
| 100 | 125(AC) | ▲ | ||||||
| 100 | 100(DC) | ▲ | ||||||
| TS125 | 125 | 122±2 | 84 | 180 | 100KA | 80 | 250(AC) | ▲ |
| 100 | 125(AC) | ▲ | ||||||
| 100 | 100(DC) | ▲ | ||||||
| TS130 | 130 | 126±2 | 88 | 180 | 100KA | 80 | 250(AC) | ▲ |
| 100 | 125(AC) | ▲ | ||||||
| 100 | 100(DC) | ▲ | ||||||
| TS136 | 136 | 132±2 | 94 | 180 | 100KA | 80 | 250(AC) | ▲ |
| 100 | 125(AC) | ▲ | ||||||
| 100 | 100(DC) | ▲ | ||||||
| TS150 | 150 | 146±2 | 108 | 180 | 100KA | 80 | 250(AC) | ▲ |
| 100 | 125(AC) | ▲ | ||||||
| 100 | 100(DC) | ▲ |
 rice cooker thermal fuse | 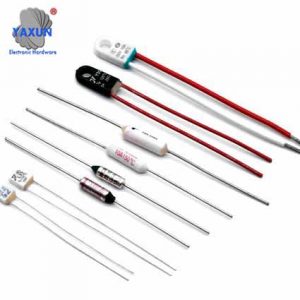 dryer thermal fuse |  electric fan thermal fuse |
Contact Us
Waiting for your email, we will reply you within 12 hours with valuable information you needed.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt