Categorii de produse
- Întrerupător termic 20
- Suport cutie siguranțe 36
- Senzor de temperatura 67
- Comutator termic 64
- Siguranță auto 19
- Siguranțe înșurubate 7
- siguranță termica 32
- siguranțe de suprafață 12
- termistor 22
- Suport pentru siguranțe montat pe PCB 27
- Ham de cabluri 6
- Suporturi pentru siguranțe cu lame 17
- termostat 46
- Siguranta electrica 14
Etichete de produs
Postări recente
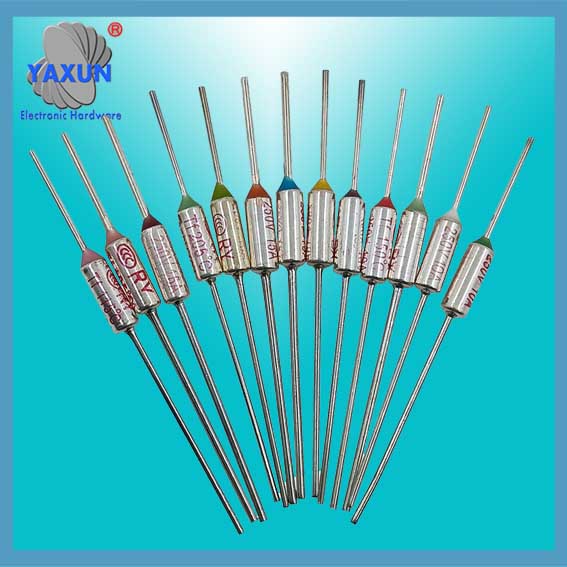
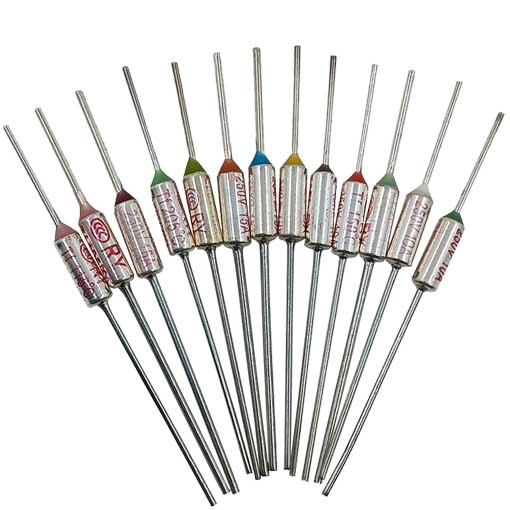
Tamura/NEC SF metal casing 15A Temperature fuse
The working principle of the AUPO / Tamura / NEC SF thermal fuse is based on the thermal expansion and conductive properties of the material. When the temperature in the circuit rises to the rated trigger temperature of the fuse, the metal material of the fuse will expand due to heat. When this expansion reaches a certain degree, it will cause the resistance inside the fuse to rise sharply.
The working principle of the AUPO / Tamura / NEC SF thermal fuse is based on the thermal expansion and conductive properties of the material. When the temperature in the circuit rises to the rated trigger temperature of the fuse, the metal material of the fuse will expand due to heat. When this expansion reaches a certain degree, it will cause the resistance inside the fuse to rise sharply. The increase in resistance will cause the fuse to heat up rapidly, further accelerating the expansion of the metal material. When the expansion reaches a certain degree, the fuse will disconnect in the circuit, thereby protecting the circuit and equipment from damage due to overheating.
Under normal circumstances, when the current passes through the thermal fuse, the fuse will maintain a low resistance state and will not affect the circuit.
When overheating occurs in the circuit, the thermal fuse begins to work. Its metal material expands due to heat, causing the resistance inside the fuse to change.
As the resistance rises, the fuse temperature rises further, accelerating the expansion of the metal material.
When the metal material expands to a certain extent, the resistance inside the fuse will rise sharply, causing the current in the circuit to be cut off.
After the fuse is disconnected, a new fuse needs to be replaced to restore the normal operation of the circuit. This is because it is difficult for the metal material to return to its original state after expansion, so that the resistance always remains high.
2. Structural features
Thermal fuse is a temperature sensing circuit cutting device with the characteristic of one-time fusing, adică, it only acts once at the fusing temperature and cannot be used again. Common types of thermal fuses include organic thermal fuses and alloy thermal fuses.
Taking the organic thermal fuse as an example, its structural features mainly include components such as temperature sensing block, compression spring and star spring. When the temperature around the organic thermal fuse rises to its operating temperature, the temperature sensing block will melt, and the compression spring will relax to make room, so that the star spring is pushed away to contact the pin, thereby disconnecting the current path. În acest fel, the circuit will be permanently cut off.
Product Features of Thermal Fuse
SEFUSE temperature fuse installation precautions:
1. When using lead bending, it should be bent from a part more than 6 mm from the root; When bending, do not damage the roots and leads, and do not pull, presa, or twist the leads forcibly.
2. When the thermal fuse is fixed by screws, riveting or binding posts, it should be able to prevent mechanical creep and poor contact.
3. The connecting parts should be able to work reliably within the working range of the electrical product without displacement due to vibration and shock.
4. When welding the lead wire, the heating humidity should be limited to a minimum, and no high temperature should be applied to the thermal fuse; Do not forcibly pull, presa, or twist the thermal fuses and leads; after soldering, cool down immediately for more than 30 secunde.
5. The thermal fuse can only be used under the conditions of the specified rated voltage, current and specified temperature. Pay particular attention to the maximum continuous temperature that the thermal fuse can withstand.
Nota: Nominal current, lead length and temperature can be designed according to customer requirements.
LE series Thermal Fuse (15A)
Caracteristicile produsului
Using temperature fuse metal casing and sense temperature organic particles.
Belonging unrecoverable type thermal fuses. Temperature fuse melting off, even if the surrounding temperature falls, it will not be turned on.
No lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd), and comply with RoHS.
REACH does not contain the specified 46 categories SVHC (SVHC).
Product Size
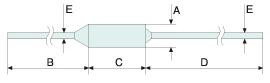
250V 15A Temperature fuse
| Lungimea cablului | Dimensions (mm) | ||||
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| Standard LE | 4.0±0.1 | 20±3 | 10.1±3 | 35±3 | 1.0±0.1 |
| Long LE(L) | 4.0±0.1 | 38±3 | 10.1±3 | 35±3 | 1.0±0.1 |
| Model | Rated temperature Tf(℃) |
Operating temperature (℃) |
Curent nominal (A) |
Tensiune nominală (V) |
maintaining the temperature Th(℃) |
Maximum temperature limit Tm(℃) |
| LE070 | 73 | 71±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 50 | 150 |
| LE073 | 77 | 74±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 50 | 150 |
| LE080 | 84 | 80±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 50 | 150 |
| LE090 | 94 | 91+3/-2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 65 | 150 |
| LE095 | 99 | 95±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 71 | 150 |
| LE108 | 113 | 109±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 85 | 150 |
| LE117 | 121 | 117±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 95 | 160 |
| LE124 | 128 | 124±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 102 | 160 |
| LE128 | 133 | 129+3/-2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 105 | 160 |
| LE138 | 142 | 138±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 110 | 160 |
| LE152 | 157 | 152±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 130 | 175 |
| LE169 | 172 | 167±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 145 | 190 |
| LE189 | 192 | 189±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 165 | 300 |
| LE213 | 216 | 213±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 190 | 300 |
Contactaţi-ne
Aștept e-mailul dvs, vă vom răspunde în termen 12 ore cu informații valoroase de care aveai nevoie.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt


